Hertz (Hz) in music refers to sound wave frequencies, which define the pitch of notes. Understanding music Hertz helps with tuning instruments and creating desired sounds. This article explains what Hertz is and how it applies to music.
What is Hertz in Music?
The measurement of sound wave frequency is captured in hertz (Hz), which indicates how many cycles a sound wave completes per second. To clarify, 1 Hz correlates with one cycle of vibration every second. Within the sphere of music, Hertz is key to shaping musical notes as it helps establish both their speed and intensity. For musicians working on tuning instruments or striving for music tuned at precise frequencies to elicit specific emotional reactions, understanding these values often denoted as abbreviated “hz” is essential.
How frequently particles within a medium vibrate due to a sound wave informs us about the frequency of that waveform. Taking pitch as an example—this elemental component in creating music has intrinsic links to its corresponding frequency.
With this deep-rooted relationship between hertz and musical notes at play, musicians can skillfully weave together rhythm, melody, and harmony into stunning works of auditory artistry. Whether it involves an individual musician meticulously calibrating their guitar or synchronizing every instrument across an entire orchestra ensemble—the mastery over concepts such as Hertz proves indispensable for crafting soul-stirring musical compositions.
The Science Behind Musical Frequencies
At the heart of every musical experience lies the science of sound waves and frequencies. Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), represents the number of vibrations per second. Different frequencies correspond to distinct pitches, and the human ear can hear sounds as low as 20 Hz and as high as 20,000 Hz.
This range lets us listen to sounds from the deep rumble of a low bass bass guitar to the high-pitched trill of a flute, creating a rich tapestry of noise that varies widely and is present.
Frequency and Pitch
Sound waves create musical notes by oscillating at distinct frequencies, which are intrinsically linked to the pitch our ears detect. The sound wave frequency determines the note’s pitch: higher frequencies yield notes with sharper pitches and brighter tones, while lower frequencies produce notes that have a softer pitch and richer resonance. This concept is essential in both designing and playing various instruments.
For instance, stringed instruments like guitars generate sounds when their strings vibrate at certain tuned frequencies that align with different musical notes. By adjusting a string’s effective length on such an instrument, one can vary its vibratory frequency—and its pitch—among other acoustic instruments as well.
In parallel fashion, wind instruments achieve variations in pitch through modifying the air column length within them, thereby changing the sound wave frequency they emit. These changed frequencies—which stem from how an instrument is constructed as well as player technique—are what give each musical note from these instruments their distinctive timbre and intonation.
Amplitude and Loudness
The loudness of sound is primarily dictated by its amplitude. When the amplitude increases, loudness follows suit—specifically, a 10 decibel (dB) increase results in the perceived volume doubling. To shape their audio’s dynamic range, which can vary from gentle murmurs to thunderous climaxes, musicians and audio engineers carefully adjust this aspect.
During music production, charts detailing sound frequencies prove essential. These visual aids are instrumental for musicians when they aim to refine their mix and elevate the overall auditory quality of their tracks. By adeptly handling both frequency and amplitude adjustments, artists have the ability to forge an engaging sonic experience that ensnares audiences’ attention.
The Role of Hertz in Different Instruments
Every instrument generates sound at distinct frequencies that are determined by its design and physical properties. It is these specific frequencies that create the unique timbre of an instrument, ranging from the profound echo of a double bass to the crisp sounds emitted by a piccolo.
Musicians utilize their knowledge of Hertz to precisely tune their instruments, which guarantees flawless harmony during a musical performance.
String Instruments
Stringed instruments like guitars produce their distinct sound through the vibrations of strings at certain frequencies, which depend on how tight and long the strings are. Guitar players must be aware of the exact frequency each note represents to tune their instrument correctly. When tuning is accurate, it ensures that all notes come together in musical harmony. Tone generators play a vital role by providing specific frequencies for proper instrument calibration.
During music production, tone generators are essential for aligning frequencies precisely, which is key to creating an accurate sound profile. Whether performing live or laying down tracks in a recording studio, musicians rely on these tools to maintain perfect harmony throughout their music. This attention to detail provides listeners with an uninterrupted and cohesive auditory experience.
Wind Instruments
Wind instruments, such as trumpets and flutes, create sound through the vibration of air within them. The construction of these instruments greatly determines the sound they produce. Factors including their material, length, and design influence the frequencies emitted. These particular frequencies are molded by various tuning standards that help integrate wind instruments into musical compositions.
By modifying the length of the column of air inside them, musicians can change a wind instrument’s pitch to alter its frequency output. This ability to adjust combined with each instrument’s distinctive build enables an extensive variety in musical expression and harmonies that enhance the ensemble soundscape whether in an orchestra or band setting.
Percussion Instruments
Instruments designed for percussion generate sound when hit, shaken, or scraped, with rhythm being their core attribute. The intervals at which these instruments are played define the rhythm, leading to a variety of patterns and beats based on the timing of each strike. The pitch produced by percussion instruments is influenced by their frequency that varies according to the instrument’s size and material composition.
The unique interaction between rhythm and frequency within these instruments gives rise to specific beat patterns and sounds that enrich musical compositions. From the resonant boom of a bass drum to the crisp crackle of a snare drum, percussion adds layers of complexity and movement to any piece of music they accompany.
Tuning Standards: 440 Hz vs. 432 Hz
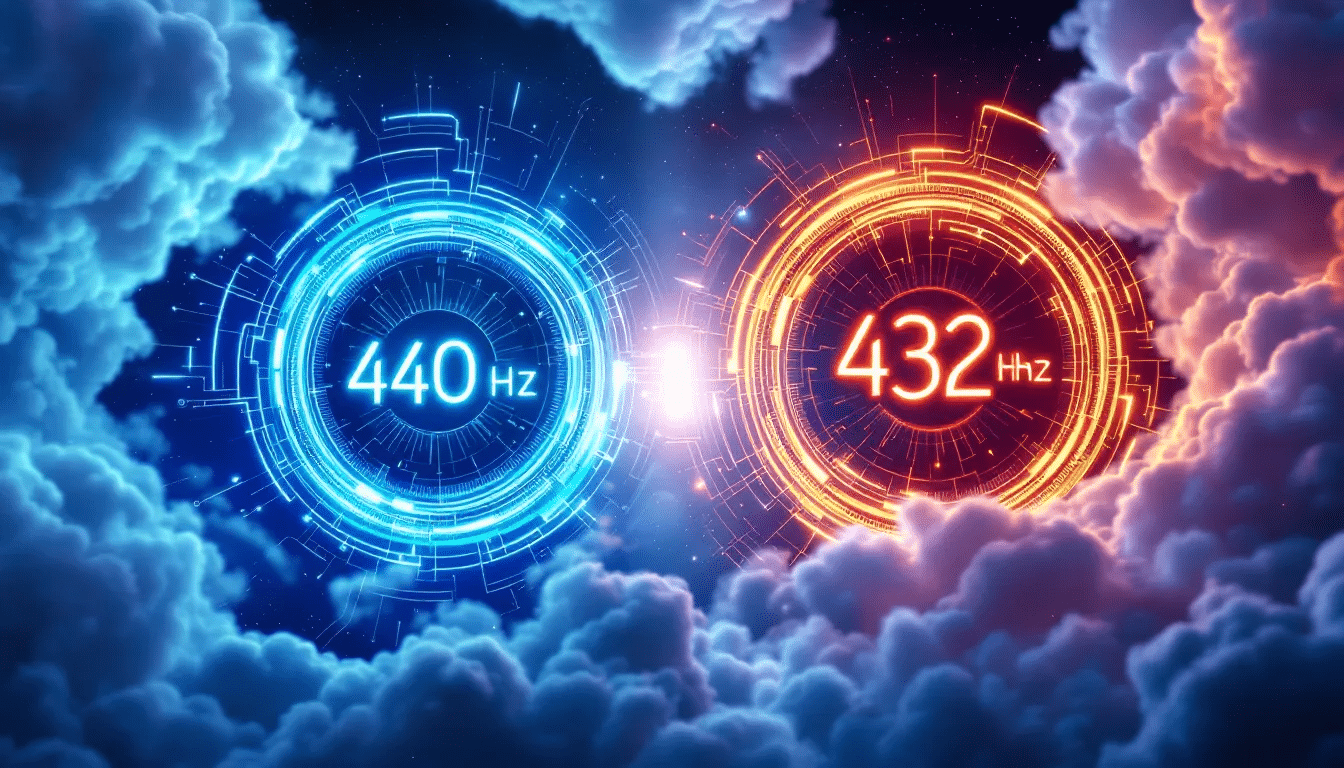
Music tuning standards typically center on 440 Hz, which is widely accepted as the standard frequency for tuning. Specifically, it designates the pitch of A above middle C and ensures uniformity in music performances and recordings by adhering to this established reference point.
Conversely, some musicians find that tuning to 432 is preferable. Hz creates a more harmonious sound they believe aligns better with natural vibrations, fostering feelings of tranquility and balance. The decision between using 440 Hz or 432 Hz was made. The frequency of tuning is ultimately based on individual preference and varying tastes among musicians.
There’s an argument suggesting that listening to music tuned at 432 Hz provides a calming effect that enhances listener enjoyment. This has made it notably favored within genres aimed at meditation and relaxation practices due to its potentially soothing qualities.
Therapeutic Uses of Music Hertz

Music has long been recognized for its therapeutic properties, and certain Hertz values are known for their stress-relieving and tension-alleviating properties. Specific frequencies in music can have a profound impact on emotional and mental well-being, offering comfort and rejuvenation to listeners.
Here, we explore the beneficial effects of healing frequencies and meditation music.
Healing Frequencies
It is thought that the 528 Hz frequency can improve mental sharpness and diminish feelings of nervousness. When one listens to this specific frequency, it tends to elevate self-assurance and cognitive clarity while also alleviating tension and worry. In a similar fashion, the 396 Hz frequency has connections with lessening sensations of dread and unease, creating an effect that grounds individuals. Frequencies such as these, especially those within the Solfeggio scale, are reputed to impart a range of emotional and physical health advantages.
The human body reacts to particular frequencies. Hence these restorative frequencies have utility in promoting psychological equilibrium along with physiological wellness. The inclusion of these frequencies into healing modalities can potentiate calmness and foster recovery processes.
Meditation Music
The track ‘Hina’ from the theta sleep music series is specifically crafted to promote a state of serenity and relaxation. Recognized as the most tranquil composition within this collection dedicated to nighttime deities, it harnesses calming theta frequencies to induce profound tranquility and offer solace through its gentle tunes.
Music tuned to particular frequencies can provide an auditory sanctuary reminiscent of nature’s harmony. Taking ‘Hina,’ named after the moon goddess, as an example, this song simultaneously calms both oceanic waves and emotional states by augmenting listener experiences with harmonious soundscapes.
To discover more about how this meditation piece facilitates deep peace, additional information on ‘Hina’ can be found at https://orchestralmeditations.com/hina-theta-sleep-meditation-personal/.
Practical Applications in Music Production
In the realm of music production, grasping and employing hertz is essential for crafting mixes that sound professional. By manipulating hertz, producers are able to precisely adjust sounds, thus achieving both clarity and exactness in their audio mixing endeavors.
The following part explores two key uses: it discusses how tone generators can be utilized as well as the implementation of the equal-tempered scale.
Using Tone Generators
A tone generator produces a sound or audio signal, utilizing digital or analog methods. These devices are capable of crafting an assortment of frequencies that assist in synchronizing sounds within the realm of music production. It’s vital for these frequencies to be aligned correctly to ensure the produced sounds blend together seamlessly and maintain clarity.
In pursuit of precise sound generation, tone generators serve as indispensable instruments in musical composition. They enable musicians and producers to fine-tune their tracks accurately, ensuring they are well-balanced. In conjunction with synthesizers, these tools enhance overall audio quality by delivering perfectly tuned music elements.
Equal-Tempered Scale
The equal-tempered scale is a system in which the frequency of each note within an octave is uniformly adjusted to achieve harmony throughout the musical spectrum. By segmenting an octave evenly into twelve parts, it enables instruments to produce sounds that are harmoniously aligned across different keys. This scaling method ensures regular spacing between notes and octaves, providing musicians with the flexibility to perform in any key.
This particular scale plays a crucial role in contemporary music creation as it offers uniform tuning for a variety of instruments. The adoption of the equal-tempered scale has been pivotal in fostering coherent performances and resolving notable issues related to tuning, thus proving indispensable for crafting exquisite music.
Summary
Understanding the role of Hertz in music opens up a world of possibilities for musicians and listeners alike. From the science behind musical frequencies to the practical applications in music production, Hertz helps shape the music we love. Whether you are tuning a guitar to 440 Hz or exploring the calming effects of 432 Hz, the knowledge of Hertz enhances our appreciation and mastery of music. Embrace this understanding, and let it inspire your musical journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Hertz in music?
Hertz (Hz) is the unit that measures sound wave frequencies, indicating how many cycles occur per second, which directly affects the pitch of musical notes.
Therefore, a higher frequency in Hertz corresponds to a higher pitch in music.
How does frequency relate to pitch in music?
Frequency directly influences pitch in music; higher frequencies produce higher pitches, while lower frequencies result in lower pitches.
What are the benefits of using 432 Hz tuning?
Using 432. Hz tuning enhances harmony and is believed to resonate with natural vibrations, promoting a greater sense of peace and overall well-being.
Therefore, it may provide an uplifting auditory experience.
How do tone generators assist in music production?
Tone generators assist in music production by producing precise frequencies, which helps align sounds harmoniously and ensures accurate sound production.
This capability is essential for achieving a polished and well-balanced musical composition.
What is the equal-tempered scale?
The equal-tempered scale is a method of tuning that splits an octave into 12 uniform segments, allowing instruments to keep their harmonic integrity in multiple keys.
This numerical modification facilitates smooth key changes and improves the adaptability of music.



